Google Play’s 16KB page-size requirement is now officially in effect. As of November 1, 2025, all new apps and updates targeting Android 15+ must support 16KB page sizes, or they will crash on upcoming high-end devices.
If your app uses native code, the only way to stay compatible with the current and future smartphones is to:
- Rebuild your binaries with NDK r28+
- Make sure the 16KB ELF segment alignment
- Test your APK in a 16KB Android 15 emulator and verify it with zipalign
This guide walks you through exactly how to check, fix, and validate your app so it continues to run smoothly on next-generation 16KB devices.
What Is the 16KB Page Size Requirement?
Android 15 introduces support for 16KB memory pages, and Google Play now requires that all native binaries inside your APK/AAB are aligned to a 16KB boundary.
This applies specifically to ELF segments in your .so files.
Who is Impacted?
This requirement primarily affects apps that use native code. If your app relies only on code written in Kotlin or the Java programming language, including all its SDKs and libraries, you are likely already compliant.
You need to take action if your app uses any form of native code, including:
a. C/C++ code built with the Android NDK
b. Third-party SDKs that come out with .so libraries
c. Game engines or custom native libraries
d. Any dependency that bundles native binaries
These native binaries must have their ELF segments (Executable and Linkable Format) already compatible with the 16KB boundary.
Why is Android Moving to 16KB Pages?
1. OEM Hardware Trends
Latest flagship devices with ARMv9 offer multiple page size configurations, and OEMs are increasingly experimenting with and adopting 16KB builds to improve memory efficiency on high RAM devices. Supporting both 4KB and 16KB adds kernel and vendor fragmentation, increases BSP maintenance, and complicates long-term updates. Standardizing on 16KB helps unify the arm64 ecosystem and simplifies future platform work.
2. Better System-Level Performance
16KB produces measurable gains at the system level, especially for large apps and workloads with high memory churn:
- Fewer page faults
- Better TLB reach
- Lower kernel memory overhead
- Faster cold starts under pressure
More than apps, these upgrades are systemic and align Android with modern ARM memory architectures.
3. Preparing for 16KB-Only Configurations
Some upcoming ARMv9 device configurations may be available with 16KB as the only supported page size.
Any native code that assumes 4KB pages, performs manual offset calculations, or ships with unaligned ELF segments risks:
- Native library load failures
- Crashes on startup
- Undefined behavior on 16KB devices
Google’s requirement makes sure that apps built today will continue to run on tomorrow’s hardware.
4. Reducing Play Store Fragmentation
Similar to the 64-bit transition or API level enforcement, Google is tightening compatibility to reduce ecosystem fragmentation. Just to make sure, all new and updated apps targeting Android 15+ must be 16KB-compatible.
With this, what will developers get?
The app doesn’t require a redesign. Once the platform moves to 16KB pages, the benefits are:
- Faster app launches (up to ~30% on affected devices)
- Lower power draw
- Smoother system performance
- Better behavior under memory pressure
Your only responsibility is to ensure all your native code and third-party .so files are built and aligned correctly for 16KB.
What Happens If Your App Is Non-Compliant?
a. App Instability Update Your Build Toolchain Crashes: This step serves as the core Android 16KB page size fix for native code. If your app or its dependencies contain native code not aligned to 16KB, it may fail to work on devices with 16KB pages, causing crashes or runtime errors at launch.
b. Exclusion from Future Devices: Apps that are not 16KB-compliant will not run on devices using 16KB, limiting access to high end devices with 8GM RAM or more.
c. Memory Inefficiency: Apps that partially rely on a 4 KB page size may cause the kernel to allocate a full 16KB page, leading to wasted memory and reduced performance.
Unsure Why Your App Fails to Launch on New Android Phones?
We handle native library fixes, NDK updates, ELF alignment, and 16KB testing to prevent startup crashes.
Guide to 16KB Compliance: How Can Teams Achieve Compliance?
Follow this roadmap to identify, fix, and verify 16KB alignment issues in your app.
1. Check If Your App is Impacted (APK Analyzer)
a. Open Android Studio.
b. Go to Build > Analyze APK and select your app’s APK file.
c. Look for the lib folder. Presence of .so files indicates native code.
d. Android Studio’s APK Analyzer and Lint will flag any 16KB alignment issue in the Alignment column, helping you quickly identify non-compliant binaries.
2. Update Your Build Toolchain
- Update to the latest Android SDK tools and Android NDK (r28 and higher).
- Newer NDK versions include NDK 16KB page size support, and NDK r28+ compiles 16KB-aligned by default, removing the need for manual configuration for first-party native code.
3. Resolve Hardcoded Page Size Assumptions
- Avoid hardcoding 4096 in native code, especially in mmap() calls.
- Use Runtime Functions: Replace hardcoded values with runtime functions that query the device for its actual page size:
- Use getpagesize()
- Use sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE)
In NDK r27 and higher, PAGE_SIZE is now undefined when 16KB mode is enabled, encouraging this best practice.
4. Manual Alignment and 16KB ELF Segment Alignment (For Older NDK/Build Systems)
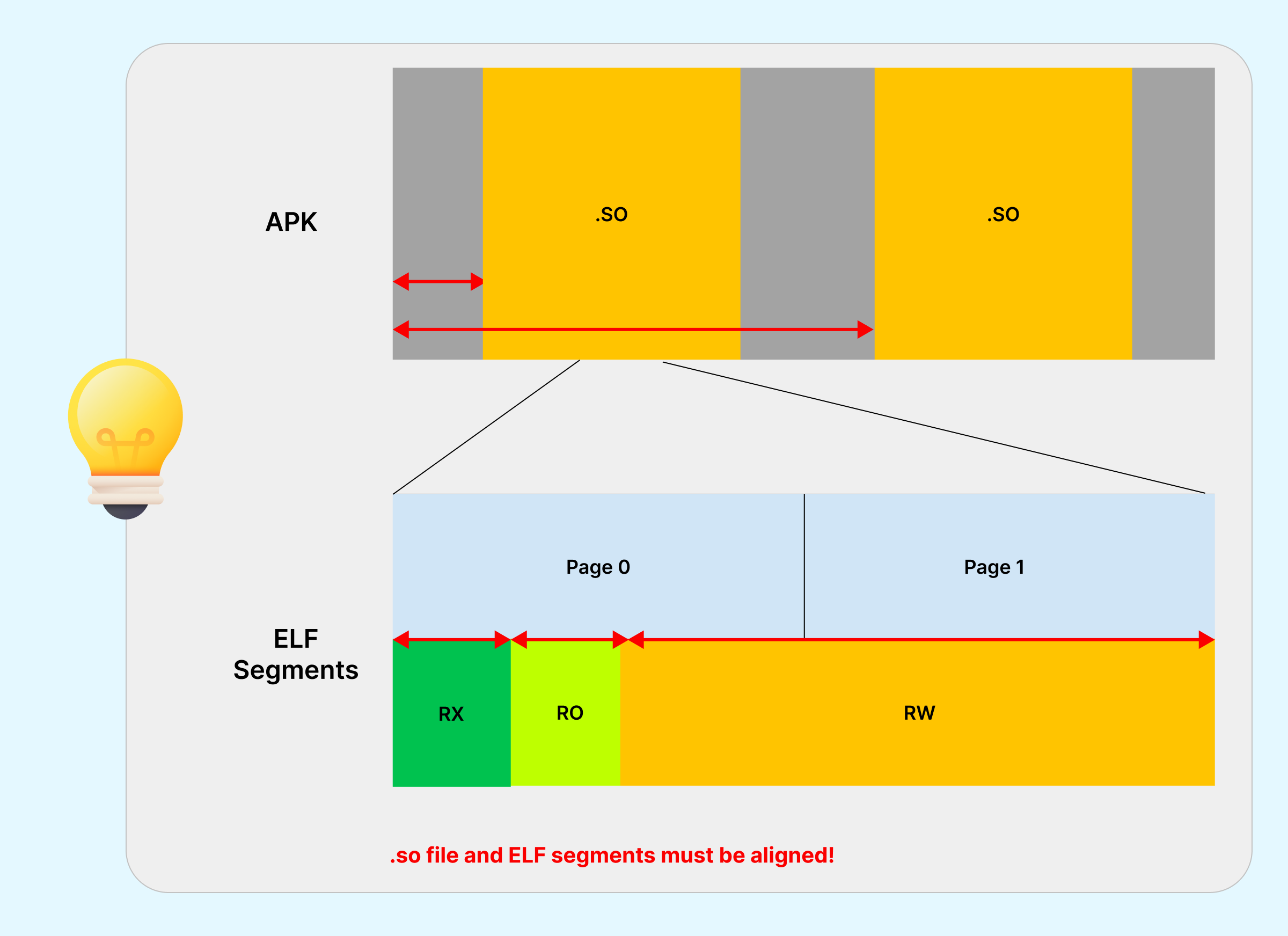
If using NDK r27 or lower, manually enable 16KB ELF alignment via linker flags:
| Build System | Configuration |
|---|---|
| CMake | target_link_options(${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-Wl,-z,max-page-size=16384") |
| ndk-build | LOCAL_LDFLAGS += "-Wl,-z,max-page-size=16384" |
| Gradle (for CMake/ndk-build) | Pass argument: -DANDROID_SUPPORT_FLEXIBLE_PAGE_SIZES=ON |
Note: Pre-built third-party native libraries must also be recompiled using a 16KB-aligned toolchain. Check with SDK providers.
5. Test in a 16KB Environment
a. Set up the Environment: Use the Android Emulator with a 16KB-based Android 15 system image, available via the SDK Manager in Android Studio.
Alternatively, enable the “Boot with 16KB page size" developer option on supported physical devices.
b. Verify Page Size: On your test device, run the following command to confirm the environment is 16KB:
adb shell getconf PAGE_SIZE
# Expected output: 16384
c. Verify APK Alignment: Use the zipalign tool to verify the final APK alignment. This step helps you check alignment using the zipalign -P 16 -v 4 command, ensuring your APK is correctly prepared for 16KB devices.
zipalign -c -P 16 -v 4 APK_NAME.apk
# The command should succeed without errors.
d. Thoroughly Test: Focus on native code-heavy areas (e.g., camera, large data operations, game physics) to catch runtime issues.
Conclusion
Google Play’s 16KB page size requirement represents a significant leap forward in Android performance optimization. More importantly, making sure the compliance for your app will make it run smoothly on the next generation of high-end Android devices.
Need assistance with Android app development and alignment issues? Absolute App Labs provides audits and fixes to keep your app running smoothly.
Technology keeps updating, and don’t let it hold back your app’s potential. Let’s make your Android application ready for the future.
